ADVERTISEMENTS:
This article provides notes on Duncan’s multiple range test.
For experiments, requiring the comparison of all possible pairs of treatment means, the LSD test is usually not suitable, when the total number of treatment is large. In such cases, DMRT is useful.
DMRT involves the computation of numerical boundaries, that allow for the classification of the difference between any 2 treatment means as significant or non-significant. This requires calculation of a series of values each corresponding to a specific set of pair comparisons. Various steps, data and analysis for DMRT are as given by Gomez and Gomez (1984).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(i) All treatment means are ranked in decreasing or increasing order.
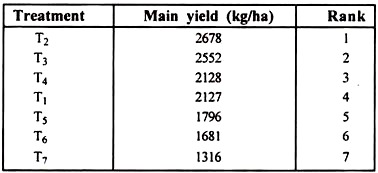
For yield etc., ranking is in decreasing order as:
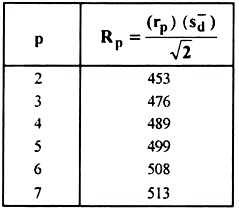
where, t is the total number of treatments, sd̅ is the standard error of the mean difference, rp values are the tabular values of the significant studentized ranges obtained from table and p is the distance in rank between the pairs of treatment means to be compared, i.e. p = 2 for the 2 means with consecutive rankings and p = t for the highest and lowest means.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
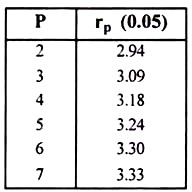
For example, under reference, the rp values with error degrees of freedom 21 and at P = 0.05 level, obtained from table (significant studentized ranges) are as follows:
The (t – 1) = 6 Rp values are calculated:
(iv) The difference between the largest treatment means and the largest Rp (the Rp value at p = t) is determined and all treatment means, whose values are less than the computed difference, are considered as significantly different from the largest treatment mean.
Similarly, the range between the remaining treatment means, (i.e. those means, whose values are larger than or equal to the difference between the largest mean and largest Rp value ) is computed and this range is compared with the value of Rp at P = m, where m is the number of treatments in the group.
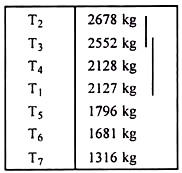
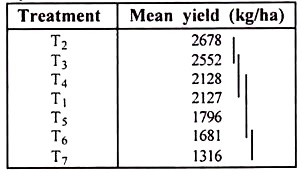
If the computed range is smaller than the corresponding Rp value, all the m treatment means in the group are declared not significantly different from each other. In the array of means arranged in ascending/descending order, a vertical line is drawn connecting all means that have been declared not significantly different from each other.
For example, in the given example, the difference between the largest Rp value (the Rp value at p = 7) of 513 and the largest treatment mean (T2 mean) of 2678 is 2678-513 = 2165 kg. From the arranged means, all treatment means except that of T3 are less than 2165 kg and hence, they are found to be significantly different from T2.
Continuation of this process further leads to as follows:
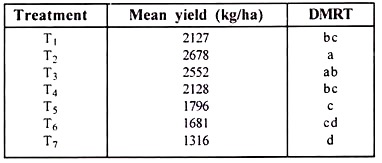
The given result could be presented using line notations or using alphabet notations. The alphabet notation can be derived from the line notation simply by assigning the same alphabet to all treatment means connected by the same vertical line. It is customary to use a for the first line, b for the second and so on.
In alphabetical notation, the representation will be as follows:
NB: Any two means having a common letter, are not significantly different at the 5% level of significance.