ADVERTISEMENTS:
The following points highlight the two important methods of reproduction in protists. The methods are: 1. Asexual Reproduction 2. Sexual Reproduction.
Method # 1. Asexual Reproduction:
It involves only one parent. All the young ones produced asexually have the same genetic constitution as that of the parent and are called clones.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Asexual reproduction can occur in the following ways:
(i) Binary Fission:
It is the division of the parent body into two equal daughter individuals by mitosis. Examples: Amoeba, Euglena and Paramecium.
(ii) Multiple Fission:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is the division of the parent organism into several daughter individuals. Examples: Amoeba and Plasmodium.
(iii) Plasmotomy:
It is the division of the multinucleate protist into two or more multinucleate offspring by the division of cytoplasm without nuclear division. It occurs in Opalina.
(iv) Spore Formation:
In some protists spores are formed for asexual reproduction. Spores have some sort of covering to withstand un-favourable conditions. On germination, each spore gives rise to a new individual. Example: Slime moulds.
(v) Budding:
In budding a small outgrowth develops from the parent body which separates and develops into a new individual. Example: Arcella (a sarcodine)
Method # 2. Sexual Reproduction:
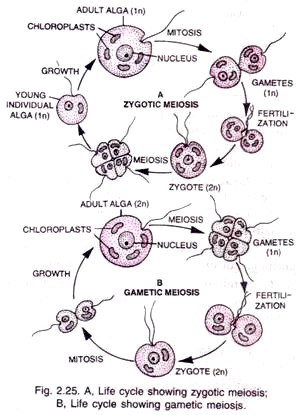
It originated in protists. Sexual reproduction involves two fundamental processes; meiosis that reduces the number of chromosomes from 2n to in and fertilization or fusion of two in gametes to form a 2n zygote (fertilized egg).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Meiosis is essential in sexual reproduction since it reduces the chromosome number to half in gametes so that after fertilization the number of chromosomes is kept constant in a species.
There are two methods of sexual reproduction:
(i) Syngamy:
It is complete fusion of two gametes to produce diploid zygotes.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Syngamy is of three types:
(i) Isogamy (two fusing gametes are similar e.g., Monocystis),
(ii) Anisogamy (two fusing gametes are dissimilar, e.g., Ceratium) and
(iii) Oogamy (large non-motile gametes are fertilized by smaller motile gametes, e.g., Plasmodium).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Conjugation:
It is temporary union of two individuals to exchange their haploid pronuclear to from a zygote nucleus. Each individual with zygote nucleus produces daughter invidious by binary fission. It occurs in Paramecium.