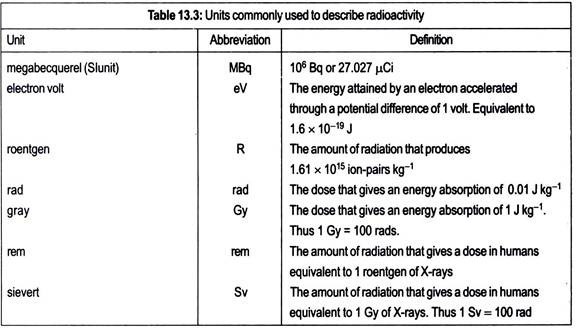
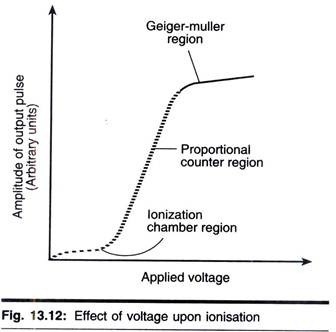
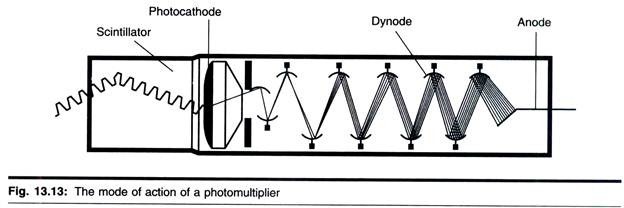
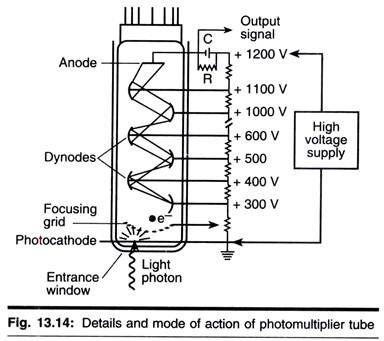
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about the Identification of Diseased Plants and Plant Parts with the help of fifteen specimens.
1. Specimen:
The infected tuber and plant shoot show the following features:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(a) The infected potato is characterised by warty and dirty cauliflower-like proliferations of abnormal tissue of variable size and shape. The plant shoot also is deformed particularly near the stolen zones. This is a case of wart disease of potato (Solanum tuberosum) caused by the pathogenic fungus – Synchytrium endobioticum (Phycomycetes) (Fig 3.39).
2. Specimen:
The infected plant parts and also tubers show the following signs and symptoms:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(a) In infected plants symptoms appear on leaflets, petioles or on stems as brownish to purplish-black lesions.
(b) The infected areas in some cases are dried, blackened and shriveled.
(c) The infected tubers show decay from the margin.
Thus it is late blight disease of potato (Solanum tuberosum) caused by the pathogenic fungus Phytophthora infestan (Phycomycetes) (Fig 3.40).
3. Specimen:
In infected plant, the following symptoms are seen in the shoot.
(a) In infected plant, prominent white pustules of variable shape and size appear particularly on the leaves, stem and inflorescence.
(b) Several pustules coalesce together to form a large patch.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(c) Mature pustules are ruptured and liberate powdery spore masses.
(d) In infected plant, stem, inflorescence axis and buds are often deformed and swelled irregularly.
It is white rust disease of crucifers like Brassica napus, B. alba etc. caused by the pathogenic fungus Albugo Candida (Phycomycetes) (Fig 3.41).
4. Specimen:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The shoot of the infected plant shows the following symptoms:
(a) In infected plant, the leaves appear to be distorted, puckered along the midrib and curled-up.
(b) The leaves become yellow to reddish in colour with gradual defoliation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(c) The buds, young inflorescences etc. are also deformed and dried up.
It is a case of Peach (Prunus sp.) leaf curl disease caused by the pathogenic fungus Taphrina deformans (Ascomycetes) (Fig 3.42).
5. Specimen:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In infected plant, the following symptoms are noticed:
(a) Characteristic sclerotia are present in the inflorescence of infected plant.
(b) Sclerotia are black, hard, horn-shaped, and localized in place of grains of the inflorescence.
Thus, it is ergot disease of rye plant (Secale cereale) caused by the pathogenic fungus, Claviceps purpurea (Ascomycetes) (Fig 3.43).
6. Specimen:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The diseased plant shows the following features:
(a) Characteristic reddish-brown and/or blackish pustules are present on the leaf blade, leaf sheath and stem sheath.
(b) The pustules at maturity coalesce with one another to form long infected streaks.
It is a case of black stem rust disease of wheat (Triticum aestivum) caused by the pathogenic fungus Puccinia graminis tritici (Basidiomycetes) (Fig 3.44).
7. Specimen:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The diseased plant shows the following symptoms:
(a) The smutted inflorescence shows deformity of entire spikelet.
(b) The grain position is filled up by black, dry, powdery masses of spores.
(c) The glumes and kernels arc completely disintegrated after emergence, of powdery mass of spores, leaving only the bare rachis.
It is a case of loose smut disease of wheat (Triticum aestivum) caused by the pathogenic fungus, Ustigago nuda var tritici (Basidiomycetes) (Fig 3.45).
8. Specimen:
The diseased plant shows the following features:
(a) In the diseased plant, heads are blackened just after emergence from the leaf sheaths.
(b) All the grains in a diseased ear are transformed into masses of spores which are held in place by persistent, tough and greyish-white membrane.
Thus, it is the covered smut disease of Barley (Hordeum vulgare) caused by the pathogenic fungus Ustilago hordei (Basidiomycetes) (Fig 3.46).
9. Specimen:
The infected plant bears the following symptoms:
(a) In the diseased plant, there is drooping, withering and finally yellowing of the upper leaves.
(b) In infected stems characteristic reddish tissues are present inside.
(c) In severe cases, the entire plant becomes dried up.
It is a case of Red rot disease of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) caused by the pathogenic fungus, Collelotrichum fulcatum (Deuteromycetes) (Fig 3.47).
10. Specimen:
The diseased plant shows the characteristic signs and symptoms in all shoot parts as stated below:
(a) All shoot parts of the infected host show the infective symptoms like brownish eye-shaped spots. The spots often vary in size and shape.
(b) The spots initially appear as small brown areas surrounded by a yellowish halo and then become dark-brown at maturity. Several spots coalesce to form a necrotic streak.
(c) The spots are present on leaves, grains and stem column.
(d) In severe cases, the leaves are dried up from the margin.
It is a case of brown spot disease of Rice (Oryza saliva) caused by the pathogenic fungus, llelminthosporium oryzae (Dcutcromycetcs) (Fig 3.48).
11. Specimen:
In diseased plant, the following symptoms are recorded from the infected leaves:
(a) Symptoms appear particularly on the leaflets of lower leaves as dark spots which, at maturity, are surrounded by a yellowish ring.
(b) The spots are circular and sometimes they coalesce to form a large spot and finally defoliation occurs.
It is a case of Tikka disease of Groundnut (Arachis hypogea) caused by the pathogenic fungus Cercospora per sonata (Deuteromycetes) (Fig 3.49).
12. Specimen:
The infected plant shows the following features:
(a) Characteristic dark brown to black, ovate to angular spots are present on the leaflets.
(b) Each spot shows centric rings and a narrow chlorotic zone is located around each spot.
(c) In severe cases, spots appear on stem and affected plants turn yellow and dry up.
It is a case of early blight disease of potato (Solanum tuberosum), caused by the pathogenic fungus, Alternaria solani- (Deuteromycetes) (Fig 3.50).
13. Specimen:
The diseased plant shows the following features:
(a) Necrotic lesions are present along the margin of the leaves or throughout the entire leaf blade or on the stem surface.
(b) The lesions are blackish brown in colour and coalesce to form rotted streaks.
It is a case of stem rot disease of jute (Corchorus capsularis) caused by the pathogenic fungus, Macrophomina phaseolina (Deuteromycetes) (Fig 3.51).
14. Specimen:
The diseased plant shows the following features:
(a) The symptoms appear on leaves, twigs and fruits as spots of light brown colour.
(b) The spots become corky and brownish, assuming a cankerous appearance at maturity.
(c) On fruits, the lesions often coalesce forming very conspicuous, irregular patches of rough, scabby raised areas.
It is a case of Citrus Cankar disease of Lemon (Citrus sps.) caused by the pathogenic bacteria Xanthomonus citri (Fig 3.52).
15. Specimen:
The infected plant shows the following features:
(a) On the leaves, there is appearance of faint circular chlorotric lesions with gradual vein clearing.
(b) At maturity, on leaves, regular crumpled blister-like areas are developed.
(c) In addition to these, various malformations like curling of leaves, mosaicness of leaf colour etc. are noticed.
It is a case of viral mosaic disease of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) caused by the plant virus TMV (tobacco mosaic virus) (Fig 3.53).