ADVERTISEMENTS:
Some of the most important types of plant tissue system and their function are as follows:
1. Epidermal Tissue System 2. Ground Tissues System 3. Vascular Tissue System.
All the tissues of a plant which perform the same general function, regardless of position or continuity in the body, constitute the tissue system. The tissues of a plant are organized to form three types of tissue systems: the dermal tissue system, the ground tissue system, and the vascular tissue system.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
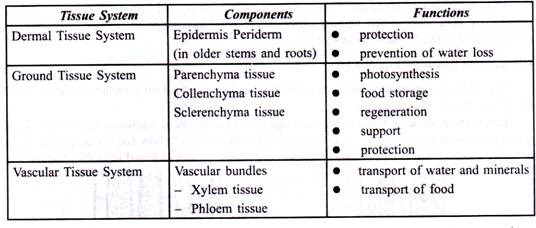
The components and functions of the tissue systems are summarized below:
1. Epidermal Tissue System:
The cells of epidermis are parenchymatous having protoplasm and nucleus without intercellular spaces. Epidermis possesses numerous minute openings called stomata. Main function of stomata is exchange of gases between the internal tissues and the external atmosphere. Cuticle is present on the outer wall of epidermis to check evaporation of water. Epidermis forms a Protective layer in leaves, young roots, stem, flower, fruits etc.
2. Ground Tissues System:
It includes all the tissues of the plant body except epidermal and vascular tissues.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is divided into following parts:
(i) Hypodermis:
It is situated below the epidermis. It is multilayered and made up of parenchymatous and sclerenchymatous cells.
(ii) General Cortex:
This consists of parenchymatous cells with or without chloroplasts.
(iii) Endodermis:
Endodermis is single layered made up of parenchymatous cells. The radial and internal walls of endodermal cell are thickened; a band of lignin or suberin knows as casparian strip is sometimes found on the radial and transverse wall of every cell.
(iv) Pericycle:
It is single or multilayered and is situated in between endodermis and vascular bundles. It is made up of sclerenchymatous and parechymatous cells.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(v) Pith:
The central portion in stems and roots is called pith or medulla. It is made up of parenchymatous cells with intercellular spaces. In dicot stem the pith is large and well developed; in dicot roots the pith is either absent or small; in monocot roots large pith is present; in monocot stem the vascular bundles are scattered and the ground tissue is not marked into different parts.
3. Vascular Tissue System:
It consists of xylem and phloem tissues which are found as strands termed as vascular bundles. The main function of xylem is to conduct water, materials to different parts of the plant body. The main function of phloem is transportation of food materials in different parts of the plant.
There are three different types of vascular bundles (Fig. 3.5):
(i) Radial Bundles:
Xylem and phloem strands are located on alternate radii in radial vascular bundles. These are mainly found in roots.
(ii) Conjoint bundles:
Xylem and phloem combine together into one bundles, Xylem lies towards the centre and phloem towards the periphery. There are two types of conjoint bundles.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Collateral:
Xylem and phloem lie on the same radius, xylem towards the centre and phloem towards the periphery. When cambium is present in collateral bundles, such bundle is called open, e.g. in dicot stems and collateral bundle without cambium is called closed, e.g. in monocot stems.
Bicollateral:
In this type of bundle, the phloem strands are present on both outer and inner side of xylem.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iii) Concentric Bundles:
In this type of vascular bundle, one tissue is completely surrounded by the other. These are of two types Amphivasal and Amphicribral.
Amphivasal:
In this type of vascular bundle xylem surrounds the phloem, e.g. Dracaena.
Amphicribral:
In this type, phloem surrounds the xylem, e.g. in Ferns.