ADVERTISEMENTS:
The below mentioned article provides an outline of a plant tissue culture laboratory.
Introduction:
Plant tissue culture is not a separate branch of plant science like taxonomy, cytology, plant physiology etc.
Rather it is a collection of experimental methods of growing large number of isolated cells or tissues under sterile and controlled conditions.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The cells or tissues are obtained from any part of the plant like stem, root, leaf etc. which are encouraged to produce more cells in culture and to express their totipotency (i.e. their genetic ability to produce more plants). Cells or tissues are grown in different types of glass vials containing a medium with mineral nutrients, vitamins and phytohormones. Therefore, to carry out the experiments using tissue culture techniques, a well-equipped laboratory is first required.
In recent years there has been a large increase in the number of research laboratories using tissue culture techniques to investigate many fundamental and applied aspects of higher plants. However, the use of these techniques is not confined to research alone.
Tissue culture techniques are being exploited by many commercial laboratories. Even many horticultural companies are setting up small units to multiply plants which are difficult to propagate by conventional means. The general organization of a tissue culture laboratory and the basic techniques will be discussed under different subheadings.
Tissue Culture Laboratory:
An ideal tissue culture laboratory should have at least two big rooms and a small room. One big room is for general laboratory work such as preparation of media, autoclaving, distillation of water etc. The other big room is for keeping cultures under controlled light, temperature and humidity. The small room is for aseptic work and for keeping autoclaved articles.
General Laboratory:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The general laboratory for tissue culture should be provided with the following articles and arrangements:
A Washing Area:
This is very important for a tissue culture laboratory. It should be provided with a large sink, running hot and cold tap water, brushes of various sizes, detergent and a bucket of single distilled water for a final rinse of the washed glass goods.
A number of plastic buckets are required for soaking the glass goods to be washed. Another separate bucket with lid is also required for disposing off the used or infected media before cleaning. Only this bucket should be kept outside the room or cleaning area and should be cleaned twice-in a week.
Hot Air Oven:
It is necessary for drying the washed glass goods. For this purpose, a number of enameled trays of different sizes are required for keeping wet glass goods inside the oven.
Refrigerator:
It is essential for storing various thermo- labile chemicals like vitamins, hormones, amino acids, casein-hydrolysate, yeast extract, coconut milk, etc. Stock solutions of salts are also kept to prevent contamination.
Distillation Plant:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
A single distillation and a double distillation water plant are indispensible. Two big plastic containers are required for storing the distilled water.
Weighing Balance:
Three types of weighing balances viz. pan balance; chemical balance and electric balance are required for weighing chemicals, sugars, agar- agar and others.
pH Meter:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is necessary for the measurement and adjustment of pH of the nutrient medium (Fig 1.1).
Vacuum Pump:
It is required for filtering liquid media, sugar solution etc. through filter apparatus using air suction.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Autoclave:
It is very important for sterilization of nutrient media, glass goods, instruments, etc. (Fig 1.2).
Working Tables:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
These are necessary for preparation of medium.
Heater:
It is needed for heating or warming the medium to dissolve agar or to melt the agarified medium.
Microscope:
Simple, compound, inverted binocular dissection microscopes are essential for various purposes. Some of the microscopes (Figs 1.3 and 1.4) should be fitted with a camera for taking photomicrograph.
Microtome:
It is needed for sectioning the cultured tissue.
Wooden Rocks:
These are required for keeping the various chemicals.
Laboratory for Aseptic Inoculation:
This room should be without any window or ventilator in order to make it dust-free. The room should be provided with double doors. The doors should have a automatic door closer. Inside floor should be fitted with a rubber mat to facilitate cleaning. For entering into the room, shoes should be left outside.
For aseptic work, a large wooden chamber (Ca, 4′ x 4′ x 7′) is made for short term work. Upper half of the side walls of the chamber is made of large glass sheets. The chamber should also have double doors provided with a door closer.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The chamber is provided with two UV (one small, one big) sterilizing lamps and a fluorescent lamp. The switches to operate them are present outside the chamber so that the lamps can be safely switched on and off. Inside the chamber the working table and shelves are made of thick glass sheets.
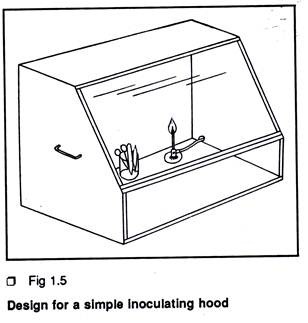
For simple routine work such as aseptic seed germination, harvesting of cultured tissue from the aseptic stock for cytological work or for microtome preparations, a small inoculating hood may be used. This can be placed on a small table at the convenient corner of the room. The figure of an ideal chamber is given here (Fig 1.5).
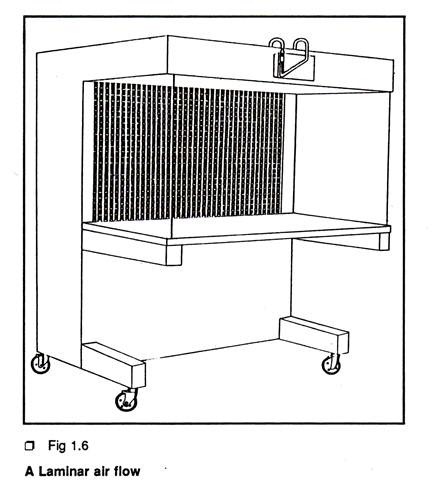
Laminar air flow cabinet (Fig 1.6) is the most suitable, convenient and reliable instrument for aseptic work. It allows one to work for a longer period which is not possible inside the inoculation chamber. Long hours of work inside the inoculation chamber may also cause suffocation and needs the interruption of work. One can work openly and easily for a longer period on the table of laminar air flow.
Laminar air flow has a number of small blower motors to blow air which passes through a number of HEPA (high efficiency particulate air) filters. Such filters remove particles larger than 0.3 µm. The ultraclean air which is free from fungal and bacterial contaminants, flows at the velocity of about 27 ±3m/minute through the working area.
All contaminants are blown away by the ultraclean air and thereby an aseptic environment is maintained over the working area. Before starting work, laminar air flow is put on for 10-15 minutes. The flow of air does not put out the flame of a spirit lamp. Therefore, a spirit lamp can be used conveniently during the work.
Culture Room:
The culture room means the room for keeping or incubating the culture under controlled temperature, light and humidity. The culture room is also fitted with double doors in order to make it dust free and to maintain a constant room temperature. One should enter the culture room keeping the shoes outside the door. To maintain the temperature around 25 ±2 ° C in-sides the culture room, air coolers are used.
This room is also provided with specially designed shelves (Fig. 1.7) to keep culture vessels. The shelves are made of glass or plywood. Flask, bottles, jars; petriplates can be placed directly on the shelves. Culture tubes can be kept on a support such as empty paper cover of fluorescent lamps. Cultures can be grown in light or in dark.
For light arrangement, each culture rack is provided with fluorescent lamps which are photo periodically controlled by an automatic timer. Racks covered with black curtains are suitable for dark incubation of culture. A thermometer and a hygrometer are fixed on the wall at the safety corner of the room to check temperature and relative humidity respectively.
The relative humidity of the culture room is maintained above 50%. Some small shelves are placed in the culture room for temporarily keeping the autoclaved articles and the culture vials containing the medium. The culture room should also have a shaker for suspension culture or single cell culture in moving liquid medium. The speed of revolution of the shaker can be controlled. The shaker is also provided with light. The platform of the shaker is fitted with clips for holding conical flasks (150 ml to 200 ml).