ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article, we will discuss about the meaning, principle, protocol and importance of the ovary culture.
What is the Meaning of Ovary Culture?
Ovary culture is a technique of culture of ovaries isolated either from pollinated or un-pollinated flowers.
Principle:
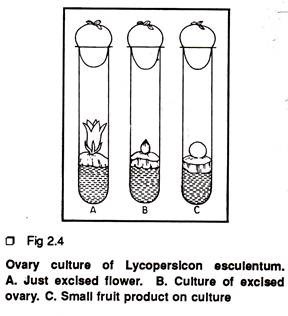
Ovary is a ovule bearing region of a pistil. Excised ovaries can be cultured in vitro. For many species e.g. tomato, gherkin (Cucumis anguria) excised ovaries grow in culture and form the fruits that ripen and produce viable seeds. This development takes place on a simple nutrient medium containing only mineral salts and sucrose, provided the flowers have been fertilized two or more days before excision (Fig 2.4).
But the ovaries of un-pollinated flowers do not grow on simple nutrient medium. However, use of some synthetic auxins such as 2, 4-D, 2 4 5- T (2, 4-5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid), NOA (2, Napthoxyacetic acid) in the nutrient medium induces the development of ovaries of un-pollinated flowers.
Often, in culture, the ovaries fail to grow into full size fruits in the restricted space of culture vial. To overcome this problem, a partial sterile culture technique is devised in which only the long flower stalk is inserted into the aseptic nutrient medium through an opening in the stopper, thus leaving the ovary free to grow outside the culture vial.
Protocol:
(1) Collect the pollinated or un-pollinated flowers from a healthy plant.
(2) Wash them thoroughly with tap water, dip into 5% Teepol solution for 10 minutes and again wash to remove the trace of Teepol.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(3) Transfer the flowers to laminar air flow cabinet. Surface sterilizes the flowers by immersing in 5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5-7 minutes. Wash them with sterile distilled water.
(4) Transfer the flowers to a sterile petri dish. Using a flamed force and a surgical scalpel, dissect out the calyx, petals, anther filaments etc. of the flower to isolate the pistil. During isolation of pistils care should be taken to ensure that the ovaries are not injured in any way. Damaged pistil, should be discarded as they often form callus tissue from the damaged parts.
(5) Place the ovaries on agar solidified nutrient medium.
(6) Incubate the cultures at 25°C in a 16 hrs, daylight regime at about 2000 lux. The light is provided by fluorescent lamp.
Importance:
Ovary culture is an useful technique to investigate many fundamental and applied aspects.
Importance’s of Ovary Culture are:
(1) It is useful to study the early development of embryo development, fruit development, different aspects of fruit physiology including respiration, maturation and disease.
(2) The effect of phytohormones on parthenocarpic fruit development can be studied from the culture of un-pollinated pistil.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(3) Floral organs play a significant role in fruit development. Role of floral organs can be studied from the in vitro culture of ovary. In some cases it has been found that pollinated ovary produce the normal fruits in vitro if the sepals are not removed before culture.
However, if the sepals are removed before culture, addition of sucrose (5%) is necessary to obtain satisfactory growth of ovary in culture. In barley, lemma and palea are very important. In onion, the growth of ovaries without perianth is markedly inhibitory.
(4) In hybridization, the plant breeders face many problems such as the failure of pollen germination on the stigma or the slow and insufficient growth of pollen tube as well as precocious abscission of flowers. Ovary or pistil culture, in vitro fertilization (test tube pollination) has been used to circumvent these obstacles. In many cases, successful results of in vitro fertilization and seed formation has been obtained.
Petunia Violaceae is a self-incompatible species. But in vitro pollination and seed formation overcome the self-incompatibility. Actually, in vitro fertilization has got the immense value in plant breeding where problems of incompatibility or sterility exist as a barrier to normal sexual reproduction.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It might be possible, therefore, to produce a hybrid between two species or varieties in vitro that could not be produced under normal in vivo conditions. Ovary culture has been successfully employed to obtain hybrids of diploid Brassica chinensis and autotetraploid B. pekinensis which are normally cross incompatible.
(5) Ovary culture has also been successful in inducing polyembryony. Poly-embryo may develop in culture from the various parts of the ovary. These poly-embryos give rise to many shoots instead of a single plantlet.
(6) The process of double fertilization not only brings about the formation of embryo and endosperm, but also stimulates the development of ovary into fruit. In most apomictic plants, although there is no fertilization, pollination alone stimulates the growth of the ovary and seed. The culture of ovaries of apomicts may, therefore, help in understanding the nature of stimulus provided by pollination.