ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Pedicillariae of Starfish 2. T.S Arm of Starfish 3. L.S Arm of Starfish.
Pedicillariae of Starfish:
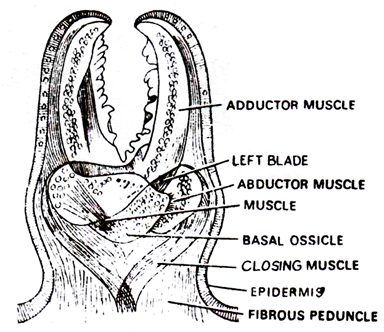
Fig. 141 STAR FISH PEDICILLARIAE JAWS
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is the slide of pedicillariae from Starfish and it exhibits following features:
(a) These are sensory organs present buried in the body-wall of starfishes and other echinoderms.
(b) They are of three types i.e., stalked, sessile and alveolar.
(c) Externally each pedicillariae is covered over with a layer of epidermis.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(d) The jaws or valves are two with one basal plate in the pedicillariae.
(e) The jaws are movable and are articulated with the stalk.
(f) The movement of jaws is controlled by a set of adductor and abductor muscles and a set of basal ossicles.
(g) Each jaw, along its internal surface is having a row of differently shaped and different sized teeth.
(h) They help in capture of food, removal of foreign objects from over the surface and also provide protection to branchiae.
T.S Arm of Starfish:
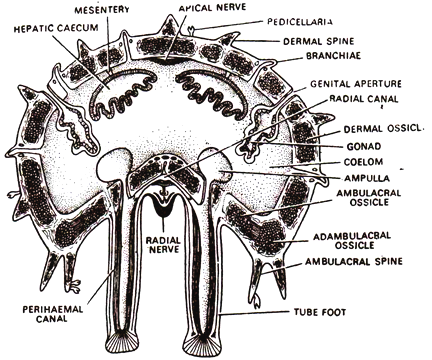
Fig. 142 T.S ARM STARFISH
It is the slide of T.S. of arm of Starfish and it exhibits following features:
(a) The aboral surface is convex and thick and oral surface is concave and thin.
(b) The whole structure is enclosed in a thick covering, which is comprised of an outer thin cuticle, an epidermis and a thick inner dermis.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(c) The epidermis, all along the aboral surface is thrown over branchiae, pedicilariae & dermal spines or tubercles.
(d) The dermal spines are supported by endoskeleton.
(e) In the dermis are present large numbers of dermal ossicles.
(g) The oral surface is having paired tubular structures — the tube feet ambulacraI spines and one pair of adambulacral ossicles.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(h) The spacious coleom is lined with coelomic epithelium.
(i) In the coelomic cavity hang a pair of pyloric caeca and a pair of gonads from aboral surface. A pair of ampullae, also, project’ into this cavity from oral surface.
(j) Tube feets are having distinct muscular suckers at their tip and are used for locomotion.
L.S Arm of Starfish:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about the structure of L. S. arm of starfish with diagram.
Fig. 143 L.S ARM OF STARFISH
1. It is the slide of L. S. of arm of Starfish.
2. It exhibits the following features:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(a) It is a some what globular structure.
(b) The aboral surface is convex and oral surface is concave.
(c) The whole structure is enclosed in a thick covering, which is comprised of an outer thin cuticle, an epidermis and a thick and inner dermis.
(d) The epidermis, all along the aboral surface is thrown into branchiae, pedicillariae and dermal spines or tubercles.
(e) The dermal spines are supported by endoskeleton.
(f) In the dermal layer are present large numbers of dermal ossicles.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(g) The oral surface is having a large aperture—the mouth, a nerve cord a layer of muscles, radial canal & gonads.
(h) The mouth leads into a spacious cardiac stomach, which opens into a pyloric stomach, which runs all along the length of the arm as pyloric diverticulum. The pyloric stomach through narrow tubular intestine opens through anus. The intestine gives off a blind rectal sac also.
(i) The pyloric diverticulum is folded along its whole length into hepatic caeca.
(j) On one side of digestive tract is present a spacious coelom which runs along the length of arm and on their other side there is present a narrow perivisceral cavity.
(k) Near the anal aperture lies a madreporite which leads below into a madreporic canal, which opens in the perivisceral cavity.