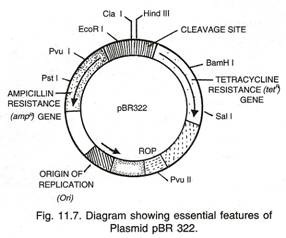
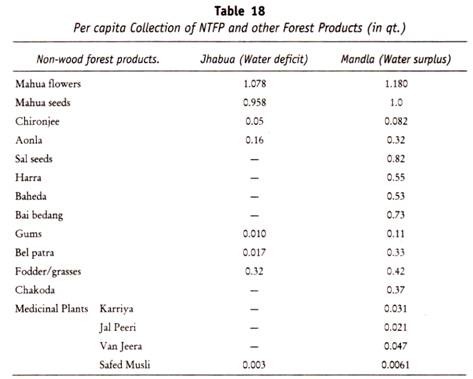
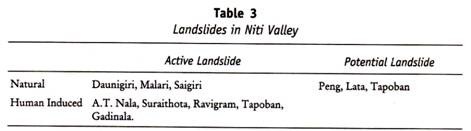
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The following points highlight the six major cardiac disorders that occurs in human body. The disorders are: 1. Heart Block 2. Ventricular Premature Beat 3. Ventricular Paroxysmal Tachycardia 4. Ventricular Fibrillation 5. Ischaemic Heart Disease 6. Myocardial Infarction.
Cardiac Disorder # 1. Heart Block:
Heart block is the condition when conduction of impulse from pacemaker area through the conducting tissue is interrupted at any degree. Sometimes impulse from S.A. node fails to reach the atrial muscle due to block (Sino-atrial block).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In E.C.G. (Fig. 7.67), P is absent due to atrial standstill, but the ventricle beats at the rhythm of the A.V. node and QRS-T complex remains unaltered. Incomplete heart block or partial heart block is the condition when the bundle of His is partially blocked.
In first degree heart block (Fig. 7.68), The P-R interval is abnormally increased from 0.16 to 0.38 sec.
In the second degree heart block (Fig. 7.70), QRS-T complex follows each second or third P wave (2:1 or 3:1 heart block). In certain partial heart block, P-R interval increases with each successive beat until one P wave is not followed by a QRS-T complex.
So in this form of heart block, the P-R interval is gradually increased in successive beats until a ventricular beat fails to occur (Fig. 7.71). This type of block is known as Wenckebach phenomenon.
Sometimes, block occurs in either branch—left or right bundle-branch by injury or by some pathological processes.
In left boundle-branch block, there is delay in activation of the left ventricle. Ventricular rate is normal, but duration of QRS complex is greater. R waves in V6 are slurred or notched.
In right bundle-branch block, there is delay in impulse conduction through the right ventricle. QRS duration is prolonged and the R waves in V1 and aVR are slurred. In V5, V6, and aVL there is late slurred S wave.
In complete heart block, where the impulse conduction is completely interrupted due to damage of bundle of His, there are complete atrioventricular dissociations. Atrium beats at the rate of sinus rhythm and ventricle at its own. This type of block is known as complete or third degree heart block. In the E.C.G., P-P interval and R-R interval will be same all throughout but P-R interval will be variable because P will not be followed by the QRS-T complex (Figs 7.69 & 7.72). Resultant cerebral ischaemia may cause dizziness and fainting (Stokes-Adams syndrome).
Cardiac Disorder # 2. Ventricular Premature Beat or Extra-Systole:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Fig. 7.73 illustrates the series of ventricular premature beat or extra-systole. Sometimes, a portion of the myocardium becomes irritable and ectopic beat occurs before the expected next normal beat. This beat causes transient interruptions of the cardiac rhythm. This type of ectopic beat is known as ventricular extra-systole or premature beat.
Cardiac Disorder # 3. Ventricular Paroxysmal Tachycardia:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
This is the condition when the ventricular muscle is damaged considerably. The E.C.G. shows the series of ventricular premature beats or extra-systole occurring successively for several beats without any normal beats interspersed (Fig. 7.74). This is the early stage of ventricular fibrillation.
Cardiac Disorder # 4. Ventricular Fibrillation:
This is the condition of massive damage at multiple areas of the ventricles. In the E.C.G., the complexes are bizarre and the individual component cannot be deciphered (Fig. 7.75).
Cardiac Disorder # 5. Ischaemic Heart Disease:
This is the condition when the circulation of the heart muscle is interfered with. In the E.C.G., there is inversion of T waves. The RS-T segments are sagged.
Cardiac Disorder # 6. Myocardial Infarction:
It is the condition when an area of the muscle is necrosed due to permanent arrest of blood supply to that area. The cause of arrest of blood supply is due to formation of thrombus in a region narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques (coronary thrombosis). The E.C.G. shows deep Q wave, S-T segment elevation and T wave inversion.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In early stage, the prominent Q wave may not be observed. Only elevation of RS-T segment in lead I, aVL and V5 -V6 may be observed. Depression in RS-T segment may be observed in leads II, III, and aVF. In old infarction, there is prominent Q wave which is observed in lead I, aVL, and V5 – V6.