ADVERTISEMENTS:
List of sixteen numerical problems on monohybrid cross.
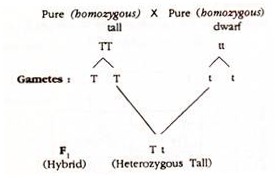
Q.1. What will be the appearance of (a) F1 and (b) F2 progenies when a pure (homozygous) tall pea plant is crossed with a pure (homozygous) dwarf pea plant?
Tallness (T) gene is dominant over dwarfness (t) gene.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Solution:
Pure (homozygous) tall pea plant = TT
Pure (homozygous) dwarf pea plant = tt
(a) Parents:
Thus, the off-springs of F1 generation will be heterozygous tall.
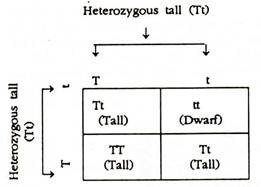
(b) Here the F1 hybrids, i.e., heterozygous tall (Tt) are self-pollinated which may result into following possibilities:
Therefore, 3 plants will be tall and one plant will be dwarf in F2 generation showing a ratio of 3: 1.
Results:
(a) The result of F1 would be the production of heterozygous tall (Tt).
(b) The result of F2 would be the production of tall and dwarf in a ratio of 3: 1. Out of 3 tall plants one would be pure (homozygous) tall (TT) and two would be heterozygous tall (Tt). The dwarf would be a pure homozygous dwarf (tt).
Q.2. When a plant homozygous for tall is crossed with a plant homozygous for dwarf, what will be the appearance of the offsprings of a cross of F1 with its tall parent.
Solution:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
When a plant homozygous for tall (TD is crossed with a plant homozygous for dwarf (tt) the off-springs in the F1 will be the production of heterozygous tall (Tt).
Now such a heterozygous tall (Tt), when back-crossed with its tall parent (TT), will show the following results:
Result:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In such a case all the parents will be tall.
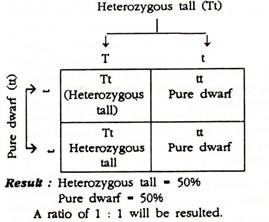
Q.3. When a plant homozygous for tall is crossed with a plant homozygous for dwarf, what will be the appearance of the off-springs of a cross of F1 with its dwart parent?
Solution:
When a plant homozygous for tall (TT) is crossed with a plant homozygous for dwarf (tt), the off-springs in the F1 will be heterozygous tall (Tt).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
When such heterozygous tall (Tt) is back crossed with dwarf parent (tt) the following will be the result:
Result:
In such cases the result would be the production of tall and dwarf in a ratio of 1: 1.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.4. Work out for the genotypes of the parents of the cross between a tall and a dwarf pea plant which result into about one half of the tall and one half of dwarf off-springs.
Solution:
Because the ratio is 1: 1, so it is a test cross between a pure dwarf (tt) and a heterozygous tall (Tt).
The genotypes may also be shown as follows:
Heterozygous tall (Tt) will form the gemetes T and t.
Pure dwarf (tt) will form the gemetes t and t.
Q.5. Work out the probabilities of the off-springs in a case when heterozygous tall hybrids of F1 generation are self-fertilized.
Solution:
Heterozygous tall hybrids are represented as Tt. Heterozygous tall (Tt)
Result:
A ratio of 3 (tall): 1 (dwarf) will be resulted. So tall off-springs will be more in number.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q.6. What will be the result in F1 generation when a homozygous white male rabbit is crossed with a homozygous black female rabbit?
Also work out the back cross.
Q.7. How can we produce such seeds which, when sown, yield pink-coloured Four O’ clock plants?
Solution:
Pink coloured Pour O’ clock plants are generally the hybrids and can be produced by crossing the homozygous red flowered plants with homozygous white flowered plants as under:
Q.8. What type of the gametes and flower colours of the off-springs would be produced in the following crosses?
Result:
A ratio of 1 (Red): 2 (Pink): 1 (White) will be produced.
Q.9. What type of gametes and the flower colours of the off-springs would be produced in the following cross?
Q.10. What type of garnets and flower colours of the off-springs would be produced in the following cross:
Di-hybrid Cross Exercises:
Q.11. What will be the result of selfing the F1 generation in a cross when round and yellow seeded pea plants (YYRR) are crossed with green and wrinkled (yyrr) seeded pea plant?
The result will be yellow round (9), yellow wrinkled (3), green round (3) and green wrinkled (1). So it shows the ratio of 9: 3: 3: 1.
Q.12. When round and yellow seeded pea plants (YYRR) are crossed with green wrinkled (y y r r) seeded pea plants the F1 are yellow and round seeded plants (Yy Rr).
What will be the results when this F1 is crossed with round and yellow seeded parents?
Solution:
Following results may be obtained when F1 (YyRr) are crossed with pure yellow and round seeded parent (YYRR).
Q.13. When round and yellow seeded pea plants (YYRR) are crossed with green and wrinkled (yyrr) seeded pea plants the F1 are yellow and round seeded plants (YyRr).
What will be the results when this F1 is crossed with green and wrinkled seeded (yyrr) parents?
Solution:
Following results will be obtained when F1 (YyRr) are crossed with green and wrinkled seeded (yyrr) parents:
Q.14. Find out the phenotypic appearance of the off-springs of the following cross, in which the genotypes of the parents are given:
yyRr X Yyrr
Solution:
It is an exercise of dihybrid ratio. It is based on the facts that yellow colour is dominant over green character, and the roundness is dominant over wrinkledness.
Q.15. Find out the phenotypic appearance of the off-springs of the following cross, in which the genotypes of the parents are given:
Result:
A phenotypic ratio of 3 (yellow round): 3 (yellow wrinkled): 1 (green round): 1 (green wrinkled) will be produced.
Q.16. Find out the phenotypic value of the offspring of the following cross, in which the genotypes of the parents are given: