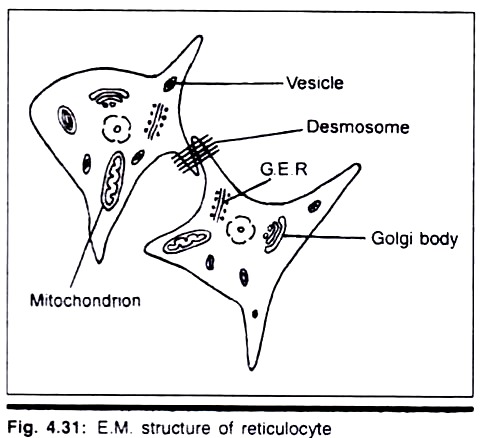
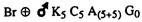ADVERTISEMENTS:
List of twenty-six general problems on genetics.
Q. 1. The round shape of pea seeds is dominant over the wrinkled shape of seeds. If two homozygous parents belonging to round and wrinkled character are crossed, then describe the F2 generation including test cross ratio.
Ans.
In the test cross, F1 hybrid (Ww) is back crossed to one of the homozygous recessive parent like-
Thus test cross ratio shall be 1 round (Ww): 1 wrinkled (ww).
Q. 2. When a red fruited tomato plant is selfed, red and yellow fruited plants are produced in the ratio of 32:10. What is the genotype of the parent?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans:
Note. In tomato red fruit colour is dominant over yellow.
Given ratio-Red: Yellow = 32: 10
Approximate phenotypic ratio = 3: 1
This 3:1 is the monohybrid ratio. The red fruited plant must be a hybrid one. The genotype is Rr. While crossing a pure bred red with pure yellow, this gives a hybrid but with red fruit.
Phenotype: 3 red: 1 Yellow
Thus, the genotype of parent is Rr.
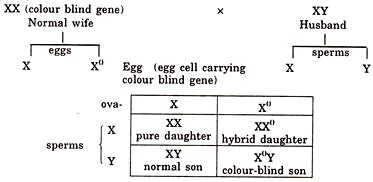
Q. 3. A normal wife carrying gene for colour-blindness marries a normal husband. Give the genotype and phenotype of their children. Further, if normal wife marries with colour blind husband what shall be their resulting generations ?
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Ans:
The wife (female) is represented by XX and husband (male) by XY chromosomes. The factors or genes for colour-blindness are present in X-chromosome.
In the first part of the question, wife (female) is carrier of colour blind gene and husband (male) is normal.
Therefore, in their generation by the marriage of normal wife (carrier) and normal husband, 50% of the sons will be normal and 50% will be colour-blind. Among daughters 50% will be pure normal and 50% normal (carrier).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
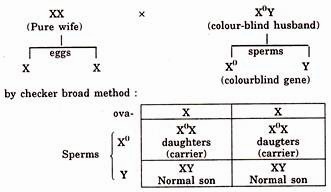
In the 2nd part of question a pure wife marries with colorblind husband.
As a result of mating.
Therefore, as a result of marriage between pure wife and colorblind husband, their total sons will be normal and daughters will be carriers for colour-blindness.
Q. 4. Albinism, the inability to synthesise chlorophyll is a recessive character over normal green colour. If a normal green tobacco plant is crossed with albino plant, the green and albino seedlings are produced in the ratio of 22: 24. Determine the genotype of the parents.
Ans:
Observed ratio = Green:albino 22:24
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Assumed ratio = phenotype = 1:1
This is the ratio of monohybrid backcross.
(i) The albino plant must have both the recessive factors for green colour gg, otherwise its phenotype will be affected. Therefore, the genotype of albino plant is gg.
(ii) The green plant must be hybrid one i.e., Gg then we get the above ratio 1:1.
This experiment is a monohybrid back cross with recessive homozygous parent.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Q. 5. In fowls the gene for black feathers B is incompletely dominant over its allele for white feather b, the heterozygous being slate blue. Determine the F2 phenotypic and genotypic ratio of a cross between a black and a white bird. What will be the result when F1 bird produced in above cross is mated to a black bird and to a white bird ?
Ans:
Q. 6. Bateson & Punnett demonstrated in sweet pea that when two white flowered varieties were crossed, F1 hybrids were all purple coloured but in F2 generation it segregated in to purple and white colour. Give the genotype of parents and grand parents.
Ans:
(9) classes 2 Rrpp : 1 rrpp
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Phenotypes 9: 7
Purple : White
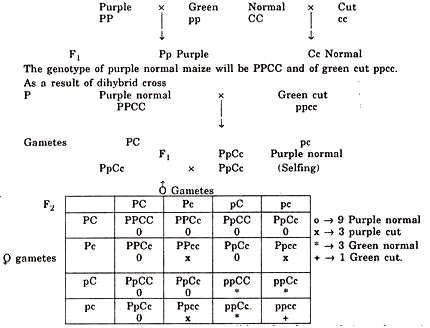
Q. 7. In maize purple colour (P) is dominant over the green colour (p) and crinkled or cut character (c) is recessive to normal character (C) of leaves. What will be the phenotype and genotype of F1 and F2 generation if purple normal maize is crossed with green crinkled.
Ans.
Thus, phenotypic ratio of F2 generation will be 9 Purple normal, 3 purple cut, 3 green normal and 1 green cut.
Q. 8. In fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, genes for normal developed wings are dominant over the genes for vestigial wings. Describe the genotypes of the parents and F2 genotypic and phenotypic ratio of the flies.
Ans:
In fruit fly the normal fly will contain V and vestigial wings will be represented by v genotype.
After self fertilization Vv x Vv, the F2 will be:
Phenotypic ratio = 3 Normal: 1 Vestigial winged
Genotypic ratio = 1:2:1.
Q. 9. In a cross between early and late rice, 3,570 early types and 1,200 late types appeared in segregating families. Find out the genotype of the parents and grand parents.
Ans:
(i) The character pair early-late is governed by a single pair of Mendelian alleles.
(ii) The segregation is taking place in the ratio of 3:1
Genotypes : 1RR : 2Rr : 1rr
Phenotypes : 3 Early types : 1 Late type
Q. 10. Tall tomato plants are produced by the action of a dominant allele ‘D’ and dwarf plants by its recessive allele ‘d’. Hairy stems are produced by a dominant ‘H’ genes and hairless stems by its recessive genes ‘h’. A di-hybrid tall hairy plant is test crossed. The F2 progeny were observed to be 118 tall hairy, 112 tall hairless, 110 dwarf hairy and 120 dwarf hairless.
(a) Diagram the cross?
(b) What is the ratio of tall; dwarf and hairy; hairless.
(c) Are these 2 loci assorting independently of one another?
Ans:
(a) This is a di-hybrid back cross ratio.
The phenotypes are as follows:
Assumed phenotypic ratio = 1:1:1:1
(b) The ratio of Tall : Dwarf = 1 : 1
The ratio of Hairy : Hairless = 1 : 1
(c) Yes. These two loci are assorting independently or freely with each other. Only because of this independent assortment four possible combinations are brought about in equal numbers.
Q. 11. A plant producing white, rotate shaped flowers is crossed with one producing cream, funnel shaped flower. Out of 76 offspring, 37 produce white, rotate shaped flowers and 39 produce cream, rotate shaped flowers. What are the genotypes of the parents?
Ans:
W = White flower
w = Cream flower
R = Rotate shaped
r = Funnel shaped.
1 (white rotate shaped) : 1 (cream rotate shaped)
Q. 12. Mating of a short tailed mouse with a normal long tailed mouse produce 1 : 1 ratio of short tailed and normal tailed mice. Crossing of two short tailed mice gives 2:1 ratio of short tail to normal tail using appropriate symbol diagram and explain these results. Is the gene for short tail a dominant or a recessive one? The gene for short tail is a dominant gene.
Ans:
Let the genotype of the short tailed mouse be—Ss and normal long tailed mouse—ss
The given 1 : 1 ratio coincides with the derived ratio.
Phenotypic ratio : 2 short tailed : 1 normal long tailed.
The dominant gene for short tail condition when present in the homozygous form (SS) is lethal to the individual. So, the individual does not survive and we have 2:1 ratio of short tailed & normal long tailed mouse respectively.
Q. 13. In case of paddy an awned variety was crossed with an awnless one. In F1 all the plants were awned but in F2 20 plants were awnless and 310 awned. How can these results be explained genetically.
Ans:
(i) Character awned-awnless is governed by 2 pair of alleles.
(ii) Assumed ratio is 15:1. This is the modified di-hybrid ratio, duplicate factors.
Q. 14. A breeder crossed two white flowered varieties of Pea. In F1 the colour of the flower appeared as pink. On raising F2 population the segregation took place as follows-
White flowered plants = 168
Pink flowered plants = 230
Ans:
The assumed ratio is modified di-hybrid cross, complementary factors. Two pairs of genes are involved to govern the flower colour. When they remain alone, they produce white flowers. But when both the dominant factors come together, they interact to produce pink colour.
Q. 15. A variety of pepper having brown fruits was crossed with a variety having yellow fruits. All the F1 plants had red fruits. When the red fruited F1 plants were crossed together, the F2 consisted of 180 plants with red fruits, 60 with brown fruits, 58 with yellow fruits and 18 with green fruits. What appears to be the genetic basis of these fruit colours in pepper?
Ans:
The fruit colour is governed by two different allelic pair of genes. Individually one dominant gene shows brown (B) and the other yellow (Y) colour. But when both the dominant genes meet together, after interaction produce red (BY) colour and the double recessive condition gives green colour (bbyy).
According to this hypothesis the segregation in F2 is in the ratio of 9:3:3:1 (interaction of genes).
Q. 16. In rice when purple pigmented plant was crossed with green pigmented plant, the F1 appeared green pigmented. In F2 the segregation of two types of pigmentation was as follows.
Purple pigment 90
Green Pigment 410
What may be the genetic basis for the segregation of pigmentation in F2.
Ans:
Here is involved inhibitory factor. The segregation is in 13:3 ratio.
Let P = Purple pigmentation
p = Green pigmentation
I = Inhibits the effect of P
i = Does not inhibit the effect of P
Q. 17. In chicken the dominant gene R gives rose comb and the dominant gene P gives pea comb. When P and R are present together the comb form is walnut. The homozygous recessives of P and R produce single comb. Determine the comb form of the offspring of the following crosses:-
Ans.
Q. 18. In summer squash the genes for white (W) colour is epistatic to that of an yellow (Y) which is dominant over green. Determine the fruit colour of the following crosses.
1- WwYy x Wwyy
2- wwYY x Wwyy
Ans:
This is the case of modified di-hybrid ratio, epistatic factor. The gene ‘W’ acts as the epistatic factor and it will produce white coloured fruits irrespective of the presence of ‘Y’ (hypostatic factor) or ‘y’. If Y is present, the fruit colour will be Yellow and if ‘y’ is present, the fruit colour will be green.
Q. 19. A large number of crosses were made between yellow coated mice.
The progeny segregated as follows:
Black Coated = 78
Yellow = 154
Explain the problem in genetical terms?
Ans:
This is monohybrid modified lethal factor (2 : 1)
Q. 20. Assume that in man the difference in skin colour between negro and white is due to two pairs of factors. AABB is black and aabb is white and that any three of the colour producing factor produce dark skin and any one colour producing factor will produce light skin. What will be the skin colour of the offspring from a mating of two individuals of F1?
Ans.
Phenotype : 1 Black : 4 Dark : 6 Intermediate : 4 Light : 1 White Progenies
Q. 21. In sweet peas C or P alone produces white flowers, the purple colour being due to the presence of both these factors. What will be the folower colour of the following crosses-
Ans.
Q. 22. In flax blue flowered plants were crossed. The offspring segregated as 48 blue, 14 white and 21 green plants. What were the genotypes of the parents?
Ans.
This is modified di-hybrid ratio supplementary factor. When both dominant genes are present it is blue. W-White dominant gene and G-Green dominant gene.
Q. 23. What would be the blood groups of the progeny of the following crosses:
(a) OO x AO
(b) BB x BO
(c) AO x AB
Ans.
50% OF THE PROGENY WILL BE ‘A’ GROUP
25% OF THE PROGENY WILL BE ‘AB’ GROUP
25% OF THE OFFSPRING WILL BE ‘B’ GROUP
Q. 24. In fowls gene for rose comb (R) and pea comb (P) if present together produce walnut comb. The recessive allele of both, when present together in homozygous condition produce single comb. What will be the comb character of the offspring of the following crosses in which the genotype of the parents are given?
(i) RrPp x Rrpp
(ii) RRPp x rrPP
(iii) RrPp x rrpp
(iv) RrPP x RRPp
(v) RrPp x RrPp
(vi) Rrpp x rrPp
(vii) RrPp x RRPp
What will be the genotype of the parent and offspring of the following crosses?
(i) Pea x Walnut → 3/8 walnut, 3/8 Pea, 1/8 rose, 1/8 single offspring.
(ii)Walnut x Single → 1/4 walnut, 1/4 rose, 1/4 pea, 1/4 single offspring.
(iii) Walnut X Rose 3/8 walnut, 3/8 rose, 1/8 pea, 1/8 single offspring.
(iv) Rose X Pea 1 walnut, 1 rose, 1 pea, 1 single offspring.
(v) Rose X Pea → 10 walnut, 15 pea offspring.
Ans.
Q. 25. In snapdragons, red flower colour (R) is completely dominant over white (r) and broad leaves (B) are incompletely dominant over narrow (b). The heterozygous condition being intermediate leaf breadth. What would be the proportion of various phenotypes in the offspring of the following crosses
(i) RrBb x rrbb
(ii) RrBb x RrBb
(iii) RrBb x RRBB
(iv) RrBB x RRBb
Ans.
Q. 26. Determine the different gametes produced by the following:
(i) Aa
(ii) AA
(iii) AaBb
(iv) Aabb
(v) AABb
(vi) AaBbDd
Ans:
(i) Aa
Gametes = A and a (2 gametes formed of different kinds)
(ii) AA → Gametes = A and A (2 gametes formed of one kind)
(iii) AaBb:
(iv) AAbb:
(v) AABb:
(vi) AaBbDd:
ABD, AbD, aBD, abD
ABd, Abd, aBd, abd
No. of gametes = 8 in tri-hybrid cross
No. of gametes = 4 in di-hybrid cross
No. of gametes = 2 in monohybrid cross