ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Meaning of Three Point Test Cross 2. Calculation of Three Point Test Cross 3. Recombination 4. Gene Sequence 5. Coefficient of Coincidence.
Contents:
- Meaning of Three Point Test Cross
- Calculation of Three Point Test Cross
- Recombination (%) of Three Point Test Cross
- Gene Sequence of Three Point Test Cross
- Coefficient of Coincidence in Three Point Test Cross
1. Meaning of Three Point Test Cross:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In a three point test cross, eight different phenotypic classes are obtained.
These eight classes are identified in two different ways, viz:
(1) By phenotypic frequencies, and
(2) By alteration of gene sequence in the genotype as a result of single crossing over or double crossing over between three linked genes.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
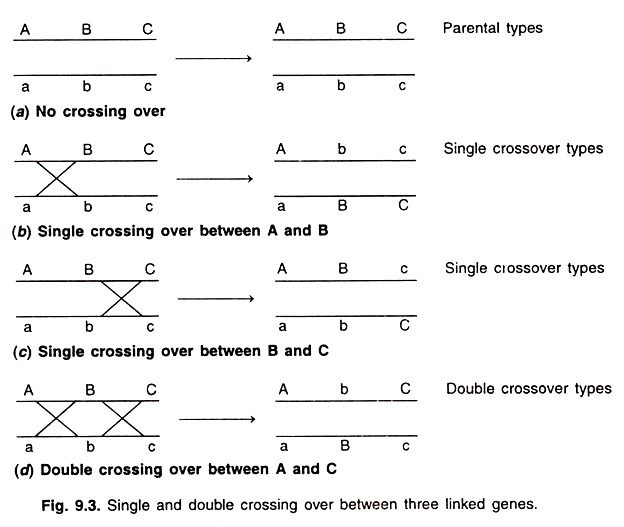
Parental types have the maximum phenotypic frequencies, double crossovers have the lowest phenotypic frequencies, and the single crossovers have phenotypic frequencies between these two classes. Suppose, ABC/abc are three linked genes located on two different chromosomes in F1 of a cross between AABBCC and aabbcc parents.
1. Single crossover between A and B will alter the position of two genes, viz., B and C (Fig. 9.3).
2. Single crossover between B and C will alter the position of only one gene, i.e., C (Fig. 9.3).
3. Double crossover between A and C will alter the position of only middle gene, i.e., B (Fig. 9.3).
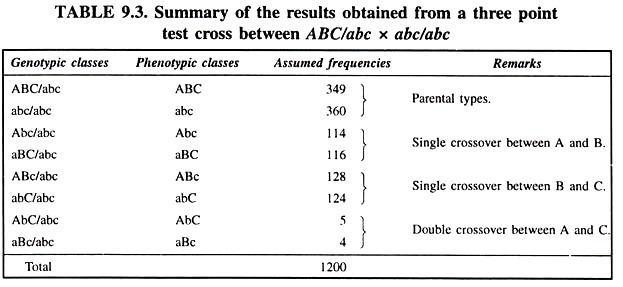
Thus eight types of gametes are produced by F1 and only one type of gamete is produced by homozygous recessive parent. Union of male and female gametes will produce eight different phenotypic classes (Table 9.3).
2. Calculation of Three Point Test Cross:
The recombination percentage or unit distance between genes is worked out by calculating the crossing over percentage between different genes. Suppose number of crossover progeny between genes A and B is P, between genes B and C is Q, between genes A and C is R, and total progeny is T. Then,
3. Recombination (%) of Three point Test Cross:
1. Between genes A and B = P + R/T x 100 = 230 + 9/1200 x 100 = 19.92
ADVERTISEMENTS:
P = 114 + 116 = 230
R = 5 + 4 = 9
2. Between genes B and C = Q + R/T x 100 = 252 + 9/1200x 100 = 21.75
Q = 128 + 124 = 252
ADVERTISEMENTS:
R = 5 + 4 = 9
3. Between genes A and C = P + Q/T x 100 = 230 + 253/1200 x 100 = 40.30
4. Gene Sequence of Three Point Test Cross:
The gene sequence is determined with the help of crossing over percentage between two genes. Greater the recombination percentage between two genes, more is the distance between them and vice versa. In this case, the maximum crossing over % is between gene A and C (40.3%).
This indicates that B is located between A and C as given below:
5. Coefficient of Coincidence in Three point Test Cross:
Coefficient of coincidence = Observed double crossovers/Expected double crossovers x 100
1. Observed double crossovers = 9/1200 x 100 = 0.75%
2. Expected double crossovers = Product of two single recombination values
= 19.92 x21.75/100 = 4.33 %
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Coefficient of coincidence = 0.75/4.33 x 100 = 17.32%
Coefficient of interference = 1 – 0.1732 = 0.8268 or 82.68%