ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about the economic importance of penicillium.
Penicillia are of tremendous economic importance. They cause considerable damage to leather goods, fabrics and furniture. Under damp conditions the wood of doors, windows and household furniture gets covered with a profuse growth of this fungus which spoils the wood.
During damp and warm weather this fungus appears on bread, cheese, butter, jam, jelly, and causes spoilage of these foodstuffs. However, the fungus is not poisonous.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
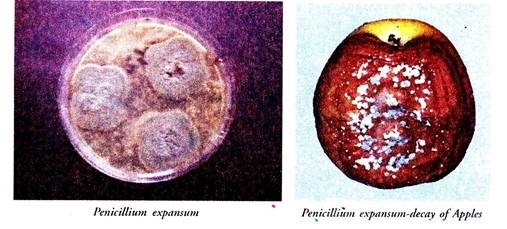
Some species such as Penicillium digitatum and P .expansum attack citrus or other fruits in storage but most others are saprophytes They cause rot and decay of lemon, orange and other fruits and vegetables in transit and storage causing loss worth of thousands of rupees each year.
P. expansum is the common agent of decay of apples in storage. The fungus gains entry through bruises and wounds. Much of the damage can, however, be prevented.
The spores cannot germinate under conditions of restricted air supply low temperature and dry conditions. Thus by proper cooling, restricted ventilation or maintaining low humidity these substances can be prevented from becoming moldy. Careful handling of fruits and vegetables so as to avoid bruises and wounds is another useful preventive measure.
Many species of Penicillium are important industrially in the production of organic acids such as oxalic, fumaric, gluconic, and citric acids. Some species such as P. roqueforti and P. camemberti are of value in food manufacture.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
They are used in cheese making to which they give not only colour and soft texture but also impart distinctive flavour and odours. P. notatum and P. chrysogenum are a source of the wonder drug Penicillin which for many has been life saver. It destroys or inactivates many pathogenic micro-organisms in persons. Some persons, however, are allergic to it. To them penicillin can be as toxic as a poison.
Griseofulvin is another antibiotic produced by P. griseofulvum. It inhibits the growth of some other fungi and is ‘thus used to control ringworm disease of animals and some fungal diseases of plants.