ADVERTISEMENTS:
The below mentioned article includes a list of five experiments in cell divisions.
1. Experiment to study the effect of colchicine on the mitotic division of the root tip cells of onion:
Requirements:
Rooted bulbs of onion, small beakers, water, 1% aqueous solution of colchicine, acetocarmine, 45% acetic acid, coverslips, slides, burner, and microscope.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Method:
1. Fill water in a small beaker and place on it a rooted bulb of onion so that the roots hang in water.
2. Fill 1% aqueous solution of colchicine in another small beaker and place on it also a similar type of rooted bulb of onion. Allow the roots to grow in both the beakers for some time.
3. Place the root tips from both the beakers on two separate slides and prepare the squash by the “acetocarmine technique” mentioned above in Exercise No. 2. Observe under microscope.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Observations:
Normal stages of mitosis are observed in the dividing cells of water-treated root tips.
On the other hand, following abnormalities are observed in the dividing cells of the colchicine- treated root tips:
(i) Separation of daughter chromosomes to their respective poles is checked in the metaphase spindles due to colchicine.
(ii) Colchicine treatment shows doubling of chromosomes in the nucleus, and thus induces polyploidy.
Results:
Colchicine, an alkaloid obtained from some species of Colchicum (e.g., C. autumnale), results in doubling of chromosomes and thus induces polyploidy in plants.
2. Experiment to study various stages of mitosis by preparing bone marrow squash of mice:
Requirements:
Chloroformed mice, razor, blade, sodium citrate (1.2%), specimen tube, needle, Camoy’s fluid, centrifuge, distilled water, HCl, water bath, ice-cold water, Basic Fuchsin stain, acetic acid, slide, cover-slips, microscope.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Method:
1. Remove the femur of a chloroformed mice, cut the epiphysis with the help of a razor or blade, and collect the bone marrow in a specimen tube containing sodium citrate (1.2%).
2. With the help of a neelde mix the bone marrow thoroughly to prepare a fine suspension.
3. Fix the bone marrow suspension in Carnoy’s fluid for about 20 minutes, centrifuge it and discard the supernatant of the centrifuge tube.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. Repeat this process of centrifuging 2-3 times by adding fresh fixative each time. This will remove the fat completely.
5. Rinse with distilled water and hydrolyze the bone marrow for 5 minutes with normal HCl on a water bath at 60°C.
6. Stop hydrolysis by immediately transferring the tissue in ice-cold water.
7. Stain the bone marrow with Basic Fuchsin for about half an hour and keep it in acetic acid (45%).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. Prepare a squash on a slide by smearing, mount with a coverslip and observe under a microscope.
Observations and Results:
Various stages of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase) are seen clearly in the actively dividing cells of bone marrow of mice.
3. Experiment to prepare acetocarmine squash of giant chromosome orpolytene chromosome from salivary glands of Drosophila:
Requirements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Drosophila melanogaster larvae, NaCl, acetocarmine solution (1%), slides, coverslips, glacial acetic acid, rubber fitted glass rod, filter paper, microscope, spirit lamp, dissection box.
Method:
1. Pick out the largest larva of Drosophila with a fine forceps, place it on a clean slide and put a drop of 0.78% saline water (NaCl).
2. Dissect out the salivary gland of the larva which is a Y-shaped, bilobed structure with thin strips of whitish fat.
3. Put the salivary gland in 1% acetocarmine stain for about 10-15 minutes, and transfer the stained gland on a slide.
4. Put a drop of glacial acetic acid (10%) on the stained salivary gland and then put the coverslip.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
5. Press it by a rubber-fitted glass rod or by thumb, heat gently and squash.
6. Use a small piece of filter paper to absorb extra fluid. Observe the slide under microscope.
Observations and Results:
Giant chromosomes of salivary gland (Fig. 40 B) are now clearly visible. These are also called polytene chromosomes. Distinct transverse bands are present on these chromosomes.
4. Experiment to prepare and study slides for meiotic stages using plant material:
Requirements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Plant material (male flowers of Bajra or Maize or some other plants), needle, acetocarmine, slides, coverslips.
Method:
1. Take the male flower buds of the given material and arrange them in a gradual sequence from smallest to largest in size.
2. Dissect out the anthers from the lowers and keep one of them in a drop of acetocarmine. Put the coverslip and press it a little with the help of needle, and observe whether any stage of meiosis is present or not. Try again and again so far you are unable to get any meiotic stage.
3. Heat a little to the slide containing any stage and squash it again by pressing it with your thumb and finger, and study the various available details.
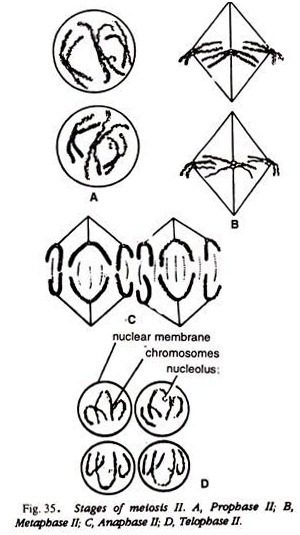
Compare and identify the stage of your slide with the Figs.: 29-35 or Fig. 38.
5. Experiment to Prepare and study the slides for mitosis using squash technique from root tips:
Acetocarmine Technique:
Requirements:
Fixed onion root tips, acetocarmine, 45% acetic acid, slides, cover-slips.
Method:
1. Cut the distal end the root tips in 45% acetic acid.
2. Stain the tips in acetocarmine and put a cover-slip.
3. Squash it by gently heating and pressing.
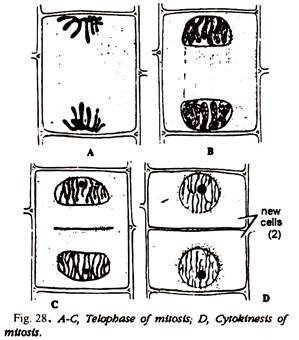
4. Study the different mitosis stages. Compare and identify with the help of the Figs. 25-28 or Fig. 38.
Aceto-orcein Technique:
Requirements:
Onion root tips, aceto-orcein solution, NHCl.
Method:
Heat gently for 5 to 10 seconds to the glass phial containing root tips and 9: 1 solution (9 parts of 2% aceto-orcein solution and 1 part of NHCl). Squash the material in a drop of 1% aceto- orcein solution. Study in under the microscope.
Compare and identify the different stages of mitosis with Figs. 25-28, 37 or Fig- 38.