ADVERTISEMENTS:
The below mentioned article provides notes on multi-enzyme complex.
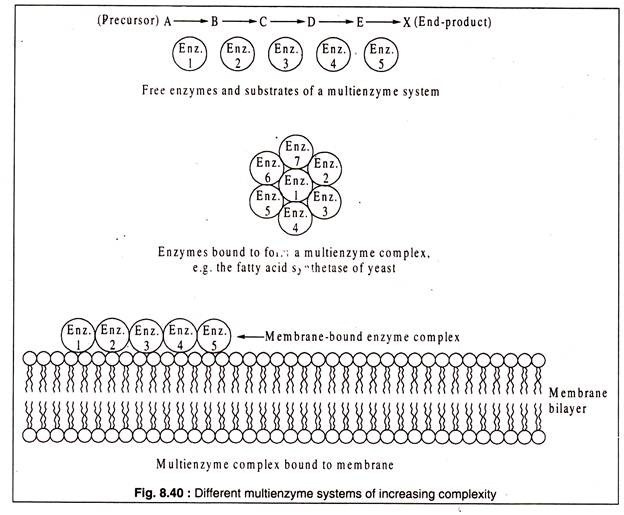
Many enzymes in living cells catalyse chains of reaction in a sequential order either in a biosynthetic or a catabolic pathway. In the preceding paragraphs hypothetical examples of such pathways have been cited. The series of enzymes catalyzing such chains of reactions are said to form a multi-enzyme system.
In its simplest form, the enzymes of such a system remain free in the cytosol as independent entities each interacting with its own substrate which is also present in -the cytosol. The product formed from each reaction is liberated and is acted upon by another enzyme of the sequence. Some of the multi-enzyme systems may operate in a different way, when the enzymes are closely associated with each other to form a multi-enzyme complex.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The fatty acid synthetase of yeast provides an example of a multi-enzyme complex. It consists of seven different enzymes which form a tightly bound cluster. Each enzyme of the complex catalyzes a different reaction, ultimately producing a long- chain fatty acid.
Not only are the enzymes bound in the complex, but also the intermediates of the synthetic pathway remain bound to it and only the final product is released. Another example is the respiratory chain enzymes. In eukaryotic cells, these enzymes form the electron transport system and are physically located in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. In the prokaryotic cells, they form part of the cytoplasmic membrane.
A diagrammatic representation of multi-enzyme systems is shown in Fig. 8.40: