ADVERTISEMENTS:
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Cold Arid Zone 2. Characteristics of Cold Arid Zone 3. Distribution.
Meaning of Cold Arid Zone:
The cold arid zone or polar desert, as a term, is commonly used to designate those polar land areas of permanent ice and the seasonally frozen lands Tundra is a Finnish term meaning ‘barren land’ or a ‘hostile territory’. In Arctic and Antarctic oceans are vast stretches of desert land i.e. desert not because of heat as the hot deserts, but because of the extreme cold.
Among the deserts the polar deserts are unique. They are in every sense the extremes of the earth. They are the domain of cold, which is the antithesis of life. The Greenland and Antarctic ice-caps are the only absolute deserts, the only utterly lifeless places.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Yet, for the globe at large, these enormous reservoirs of cold area having a world-wide influence though the people who live far from them do not realize it. But they send out their storms and their tempering chill everywhere and so shape the habitat that has nourished all life and every civilization.
Characteristics of Cold Arid Zone:
i. Aridity is the result of low temperatures prevalent throughout the year.
ii. Precipitation is low, what moisture they do receive is in the frozen form – the moisture content of air is virtually nil.
iii. The relative humidity is often quite high (75 to 85%).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
iv. Condensation consists of ice spicules floating in the air.
v. Temperatures are extremely low at all seasons.
vi. Evaporation is low and water is stored inaccessibly in the form of glaciers and ice-caps.
vii. Summer has continual daylight and winter in perpetually dark (twilight).
viii. Wind causes irregular drifting of the snow which in turn, is responsible for the mosaic like vegetation.
ix. Vegetation is scattered, occurring in small patches with mosses, lichens, ferns, grasses and bushes or totally barren.
x. The interior of continent is converted by vast glacier.
xi. The temperature of warmest month never exceeds an average of 10°C (50°F).
xii. The top soil is frozen for approximately nine months, while sub-soil is subject to permafrost.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
xiii. Physiological drought due to soil moisture being frozen.
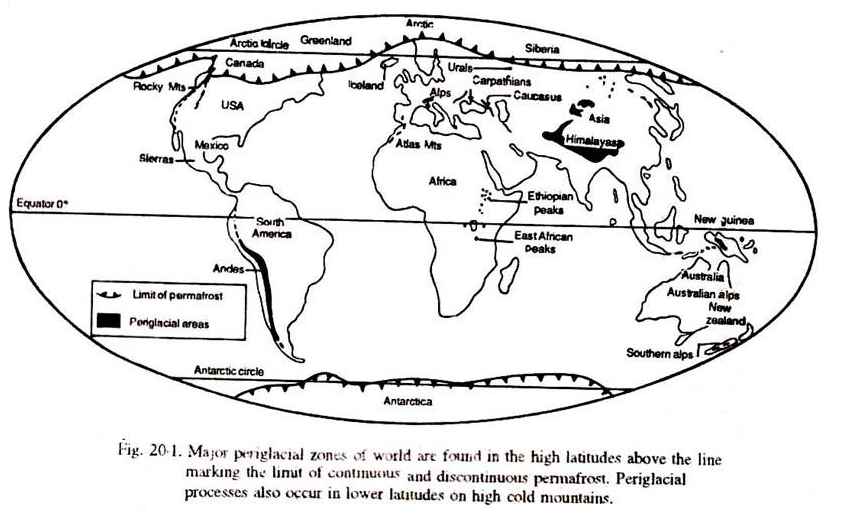
Distribution of Cold Arid Zone:
The polar arid zones are represented by the ice cap of Antarctica and Greenland, but most of the area fringing Hudson Bay and the Arctic oceans, especially the archipelago north of Canada also fall in it.
The whole of Antarctic continent falls within an area of cold arid zone. Cold desert also occurs on the peaks of high mountains of the World- Himalaya. The Greenland and Antarctica are ice-caps which remains permanently frozen.
The south polar arid zone is situated on solid land more precisely, on 3000 metres of glacial ice which in turn lies on the base rock of the Antarctic continent. At the pole this rock has been pressed down to sea level by the sheer weight of the ice sheet, which contains more than 86 per cent of the world’s ice (Store of fresh water).
Owing largely to its altitude, the south pole has by far the more severe climate. Temperatures – 140° Fahrenheit below freezing (equal to about -95° centigrade) – some 50° on the Fahrenheit scale (the equivalent to – 30° centigrade) lower than the North pole’s lowest – have been registered at or near the South pole.
At midsummer, which may lift temperatures above freezing at the North pole, rarely raises those at the South pole above zero. There the extreme cold also makes the winds more savage. They blow at velocities average 25 km an hour throughout the year. Light rays may bounce between the ice and low clouds, creating a blinding opalescence called “White out”, which wipe out every landmark.