ADVERTISEMENTS:
Cell Structure
Cells can have different shape, size, activities or functions based on the presence or absence of a membrane bound nucleus and other organelles, cells Organisms can be named as eukaryotic or prokaryotic.
Eukaryotic cell consists of a cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm. Plant cells consist of cell wall outside the cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and facilitates transport of several molecules. All the cell organelles perform different but specific functions. In animal cells controlees also form spindle apparatus during cell division. Nucleus contains nucleoli and chromatin network.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The endomembrane system includes ER, golgi complex, liposome’s and vacuoles. ER helps in the transport of substances, synthesis of proteins, lipoproteins and glycogen. The golgi body is a membranous organelle composed of flattened sacs. The secretions of cells are packed in them and transported from the cell.
Mitochondria are power house of cell, where energy produces. Mitochondria help in oxidative phosphorylation and generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). They are bound by double membrane. In plant cells, chloroplasts are responsible for trapping light energy essential for photosynthesis.
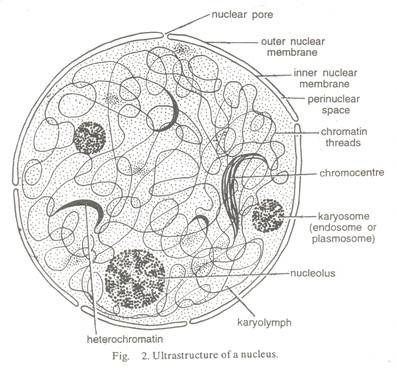
The green colored plastids are chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll. The nucleus is enclosed by nuclear envelop, a double membrane structure with nucleus is enclosed by nuclear envelop. This is a double membrane structure with nucleus pores.
Cell theory and size:
Cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms. Unicellular organisms can have independent existence and perform the essential functions of life. Anything less than a complete structure of a cell does not ensure independent living. All living organisms are composed of cells and products of cells. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. Inside each cell, there is a dense membrane bound structure called nucleus.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Nucleus used to contain the chromosomes which in turn have the genetic material known as DNA. Cells without having membrane bound nuclei are called eukaryotic. Cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus are prokaryotic. In both the type of cells, a semi-fluid matrix (cytoplasm) occupies the volume of the cell. Various chemical reactions occur in both the plant and animal to keep the cell in the ‘living state’.
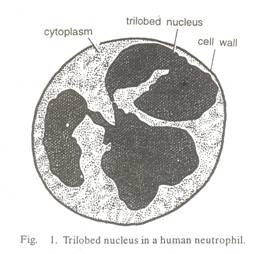
Animal cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle which is known as centriole. This helps in cell division. Cells differ in size, shape and activities. Colored image 2.1 shows those Mycoplasmas, the smallest cells, (only 0.3 um in length).
Bacteria could be of size 3 to 5 um. Human red blood cells are about 7.0 um in diameter. Among multicellular organisms. Cells may be disc-like, polygonal, columnar, cuboids, thread like, or even irregular. Fig. 2.1 shows eukaryotry cell, bacteria, PPLO and viruses.