ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss about the external morphology of cladophora.
1. Thallus is rough to touch due to the presence of chitinous material.
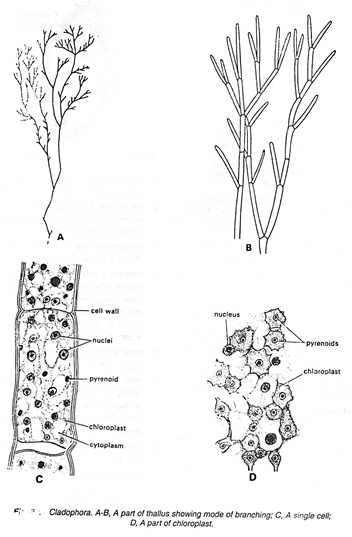
2. If seen with the help of a magnifying lens, the fine small branches of the thallus look like the branches of a small herbaceous plant (Fig. 22 A)
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Plant body is multicellular, filamentous and branched. It remains in the form of bush-like masses.
4. Thallus remains attached to the substratum by a holdfast formed by the lowermost rhizoidal cell.
5. A branch always arises just below or just above the septum.
6. Branching in Cladophora appears like a dichotomy but actually it is of lateral type. It appears so due to the process of erection, i.e., pushing of the original axis on one side.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
7. Each cell (Fig. 22B, C) is much broader in length than breadth.
8. Cell is cylindrical and remains surrounded by a lamellated cell wall, the outermost layer of which consists of chitin, middle of pectose and the innermost of cellulose material.
9. A large central vacuole is present in each cell.
10. A cell possesses either a single reticulate chloroplast or many discoid chloroplasts (Fig. 22D).
11. Many pyrenoids are present in each cell.