ADVERTISEMENTS:
In this article we will discuss the structure and functions of pili and fimbriae.
Structure of Pili and Fimbriae:
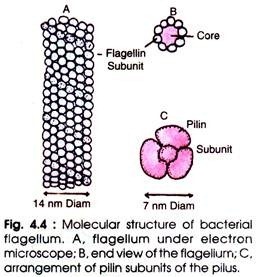
Both fimbriae and pili are like flagella as both are the appendages on bacterial cell wall. They originate from cytoplasm that protrudes outside after penetrating the peptidoglycan layer of cell wall. Fimbriae are made up of 100% protein called fimbrilin or pilin which consists of about 163 amino acids (Fig.4.4).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The number of fimbriae is around 1,000. However, a similar structure has also been observed only in Corynebacterium renale, a Gram-positive bacterium. Pili differ from flagella in being shorter and thinner, straight and less ligid. But they are in large number. They occur either at the poles of bacterial cell or evenly distributed over the entric surface of the cell. The pili are 0.2-20 µm long with a diameter of about 250 Å.
Pili are genetically governed by plasmids, the number of which varies from 3 to 5. Fimbrilin has a molecular weight of about 16,000 Daltons. In addition, the sex pili are helical tubules consisting of a hollow core (25-30Å).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The sex pili are the cylinder of repeating protein units. Its filamentous structure is governed by the sex factor (plasmid) of the bacterium for example F factor. Col I factor and R factor.
As compared to fimbriae the sex pili have a greater diameter (65-135 Å diam and length upto 20 µm), and a terminal knob of 150-800 Å diameter. There are two types of pili in E. coli for example F-pili (determined by F factor) and i-pili (determined by Col I factor. They have several receptor sites on which bacteriophages (e.g. f2, Ms2, M13, etc.) get adsorbed.
Functions of Pili and Fimbriae:
There are several functions of fimbriae and pili as given below:
(a) Bacteria containing fimbriae are called fimbriate bacteria. Fimbriae have the adhesive properties which attach the organism to the natural substrate or to the other organism. Fimbriae agglutinate the blood cells such as erythrocytes, leucocytes, eplithelial cells, etc.
(b) Fimbriae are equipped with antigenic properties as they act as thermolabile nonspecific agglutinogen.
(c) Fimbriae affect the metabolic activity. The Fim+ cells (cells containing fimbriae) possess higher rate of metabolic activity than the Fim– cells (cells devoid of fimbriae). Moreover, they function as aggregation organelles i.e. they can form stellate aggregation on a static liquid medium.
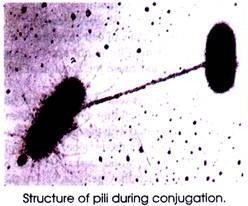
(d) The sex pili make contact between two cells. Since they posses hollow core, they act as conjugation tube. The tip of pilus recognises the female (F–) cell through which the genetic material of donor (F+) cell passes to the recipient (female) cell. Only F-pili (not I-pili) contain axial hole.